5最长回文子串
给你一个字符串
s,找到s中最长的 回文子串。
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) {
return "";
}
//定义最长回文子串的长度
int maxLength = 1;
//定义最长回文子串的起始位置
int start = 0;
//遍历可能的回文子串的中心位置
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) {
//最长回文子串的长度为奇数时,中心位置为一个字符
int oddLength = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
//最长回文子串的长度为偶数时,中心位置为两个字符
int evenLength = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int length = Math.max(oddLength, evenLength);
//找出最大长度
if (maxLength < length) {
maxLength = length;
//计算start位置
start = i - (maxLength - 1) / 2;
}
}
//截取字符串
return s.substring(start, start + maxLength);
}
//返回最长回文子串的长度
public int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length()) {
if (s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
//边界向外扩展
left--;
right++;
} else {
break;
}
}
//最后一次向外扩展不满足条件,还原该次扩展
left++;
right--;
return right - left + 1;
}
}
9回文数
给你一个整数
x,如果x是一个回文整数,返回true,否则,返回false。回文数 是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
- 例如,
121是回文,而123不是。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
// 特殊情况:
// 当 x < 0 时,x 不是回文数
// 同样地,如果数字的最后一位是 0,为了使该数字为回文
// 则其第一位数字也应该是0
// 只有 0 满足这一属性
if (x < 0 || (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)) {
return false;
}
int revertedNumber = 0;
while (x > revertedNumber) {
revertedNumber = revertedNumber * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
// 当数字长度为奇数时,我们可以通过 revertedNumber/10 去除处于中位的数
// 例如,当输入为 12321 时,在 while 循环的末尾我们可以得到 x = 12,revertedNumber = 123,
// 由于处于中位的数字不影响回文(它总是与自己相等),所以我们可以简单地将其去除
return x == revertedNumber || x == revertedNumber / 10;
}
}
14最长公共前缀
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串
""。
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if(strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
String result = strs[0];
for(int i =1;i<strs.length;i++) {
int j=0;
for(;j<result.length() && j < strs[i].length();j++) {
if(result.charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j))
break;
}
result = result.substring(0, j);
if(result.equals("")) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
}
15三数之和
给一个整数数组
nums,判断是否存在三元组[nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]]满足i != j、i != k且j != k。同时还满足
nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0。返回所有和为
0且不重复的三元组。
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) {
break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
continue; // 去重
}
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) {
L++; // 去重
}
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) {
R--; // 去重
}
L++;
R--;
} else if (sum < 0) {
L++;
} else if (sum > 0) {
R--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
16最接近的三数之和
给一个长度为
n的整数数组nums和 一个目标值target。请从
nums中选出三个整数,使它们的和与target最接近。返回这三个数的和。
class Solution {
public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int result = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
int start = i+1, end = nums.length - 1;
while(start < end) {
int sum = nums[start] + nums[end] + nums[i];
if(Math.abs(target - sum) < Math.abs(target - result)) {
result = sum;
}
if(sum > target) {
end--;
} else if(sum < target) {
start++;
} else {
return result;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
18四数之和
给一个由
n个整数组成的数组nums,和一个目标值target。请找出并返回满足下述全部条件且不重复的四元组
[nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]]
0 <= a, b, c, d < na、b、c和d互不相同nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int length = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 3; i++) {
// 跳过重复值
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 最小合都大于目标值,说明无解
if ((long) nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] + nums[i + 3] > target) {
break;
}
// 最大合小于目标值,说明i太小了,继续后移
if ((long) nums[i] + nums[length - 3] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) {
continue;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < length - 2; j++) {
// 跳过重复的数字
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 最小合都大于目标值,说明无解
if ((long) nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[j + 1] + nums[j + 2] > target) {
break;
}
// 最大合小于目标值,说明i太小了,继续后移
if ((long) nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) {
continue;
}
int left = j + 1, right = length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int x = nums[left], y = nums[right];
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + x + y;
if (sum == target) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], x, y));
// 将两个指针都往中间推移,遇到重复的数字就跳过
left++;
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) {
left++;
}
right--;
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1]) {
right--;
}
} else if (sum < target) {
// 和小于目标值,因为是排序过的,要想结果变大,左标就要往右移动,数字更大
left++;
} else {
// 同理,和大于目标值,右标就要往左移动,数字更小
right--;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
20有效的括号
给定一个只包括
'(',')','{','}','[',']'的字符串s,判断字符串是否有效。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '(') {
stack.push(')');
} else if (c == '{') {
stack.push('}');
} else if (c == '[') {
stack.push(']');
} else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) {
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
24两两交换链表中的节点
给一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。
令
cur表示当前到达的节点,初始时cur = pre。
每次需要交换
cur后面的两个节点。如果
cur的后面没有节点或者只有一个节点,则没有更多的节点需要交换,结束交换。否则,获得
cur后面的两个节点node1和node2,通过更新节点的指针关系实现两两交换节点。交换之前的节点关系是
cur -> node1 -> node2,交换之后的节点关系要变成cur -> node2 -> node1。
完成上述操作之后,节点关系即变成
cur -> node2 -> node1。再令
cur = node1,对链表中的其余节点进行两两交换,直到全部节点都被两两交换。两两交换链表中的节点之后,新的链表的头节点是
pre.next,返回新的链表的头节点即可。
node1.next = node2.next
cur.next = node2
node2.next = node1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);
pre.next = head;
ListNode cur = pre;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = cur.next;
ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
cur.next = node2;
node2.next = node1;
cur = node1;
}
return pre.next;
}
}
25K个一组翻转链表
给链表的头节点
head,每k个节点一组进行翻转,请返回修改后的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//剩余数量小于k的话,则不需要反转。
if (tail == null) {
return head;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
// 反转前 k 个元素
ListNode newHead = reverse(head, tail);
//下一轮的开始的地方就是tail
head.next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);
return newHead;
}
/*
左闭又开区间
*/
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
while (head != tail) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
26删除排序数组中的重复项
给一个 非严格递增排列 的数组
nums。请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。
元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。
然后返回
nums中唯一元素的个数。
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 1; j<nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] != nums[j]) {
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
}
27移除元素
给你一个数组
nums和一个值val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于val的元素。元素的顺序可能发生改变。
然后返回
nums中与val不同的元素的数量。
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] != val) {
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
}
}
return i;
}
}
33搜索旋转排序数组
整数数组
nums按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。给 旋转后 的数组
nums和一个整数target,如果nums中存在这个目标值target。
- 则返回它的下标,否则返回
-1。如果用二分法去分割这个数组,则肯定是一个区间为有序,另一个区间为无序。
target可以通过对左右两边界的对比,得知这个数是否在有序区间里。如果在,则对这个有序区间进行二分,如果不是,则
target肯定是在无序区间。在无序区间中二分也是一个道理,肯定回出现一个有序一个无序,然后继续判断即可,最终得出结果。
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int start = 0;
int end = nums.length - 1;
int mid;
while (start <= end) {
mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
//前半部分有序,注意此处用小于等于
if (nums[start] <= nums[mid]) {
//target在前半部分
if (target >= nums[start] && target < nums[mid]) {
end = mid - 1;
} else {
start = mid + 1;
}
} else {
if (target <= nums[end] && target > nums[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
} else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
34在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
给一个按照非递减顺序排列的整数数组
nums,和一个目标值target。
- 请找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
如果数组中不存在目标值
target,返回[-1, -1]。
public class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 0) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
int firstPosition = findFirstPosition(nums, target);
if (firstPosition == -1) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
int lastPosition = findLastPosition(nums, target);
return new int[]{firstPosition, lastPosition};
}
private int findFirstPosition(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 小于一定不是解
if (nums[mid] < target) {
// 下一轮搜索区间是 [mid + 1..right]
left = mid + 1;
} else {
// nums[mid] >= target,下一轮搜索区间是 [left..mid]
right = mid;
}
}
// 退出循环以后不能确定 nums[left] 是否等于 target,因此需要再判断一次
if (nums[left] == target) {
return left;
}
return -1;
}
private int findLastPosition(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left + 1) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target) {
// 下一轮搜索区间是 [left..mid - 1]
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// 下一轮搜索区间是 [mid..right]
left = mid;
}
}
// 主程序先执行 findFirstPosition,能执行到 findLastPosition 说明数组中一定存在等于 target 的元素,因此这里不用判断 nums[left] 是否等于 target
return left;
}
}
46全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组
nums,返回其 所有可能的全排列。
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
private boolean[] flag;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
flag = new boolean[nums.length];
backTracking(nums);
return resList;
}
public void backTracking(int[] nums) {
if (list.size() == nums.length) {
resList.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (flag[i]) {
continue;
}
flag[i] = true;
list.add(nums[i]);
backTracking(nums);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
flag[i] = false;
}
}
}
54螺旋矩阵
给一个
m行n列的矩阵matrix。请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int col = 0, cols = matrix[0].length - 1, row = 0, rows = matrix.length - 1;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int total = matrix.length * matrix[0].length;
int num = 1;
while (num <= total) {
for (int i = col; i <= cols && num <= total ; i++) { //从左到右
list.add(matrix[row][i]);
num++;
}
row++;
for (int i = row; i <= rows && num <= total ; i++) { //从上到下
list.add(matrix[i][cols]);
num++;
}
cols--;
for (int i = cols; i >= col && num <= total ; i--) { //从右到左
list.add(matrix[rows][i]);
num++;
}
rows--;
for (int i = rows; i >= row && num <= total ; i--) { //从下到上
list.add(matrix[i][col]);
num++;
}
col++;
}
return list;
}
}
57插入区间
示例 1:
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5] 输出:[[1,5],[6,9]]示例 2:
输入:intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8] 输出:[[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]] 解释:这是因为新的区间 [4,8] 与 [3,5],[6,7],[8,10] 重叠
class Main {
public int[][] merge(int[][] s, int[] k) {
int[][] result = new int[s.length + 1][2];
int index = 0,int i = 0;
//1.没有相交的情况
while(i < s.length && k[0] > s[i][1]) {
result[index++] = s[i++];
}
//2.有相交的情况
while(i < s.length && s[i][0] <= k[1]){
k[0] = Math.min(k[0], s[i][0]);
k[1] = Math.max(k[1], s[i++][1]);
}
//3.插入数组区间
result[index++] = k;
//4.剩下的也要放到数组中
while(i < s.length) {
result[index++] = s[i++];
}
//5.数组拷贝扩容
return Arrays.copyOf(result, index);
}
}
61旋转链表
给一个链表的头节点
head,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动k个位置。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 计算链表中节点个数
int len = calculateLen(head);
k = k%len;
// 慢指针初始指向头节点
ListNode slow = head;
// 快指针初始指向头节点
ListNode fast = head;
// 快指针先向前移动k步
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
fast= fast.next;
}
// 快慢指针同时向前移动,直到快指针指向的节点的
// 下一个节点为null
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 快指针此时在链表末尾
// 然后其指向的节点的后继指针指向头节点
// 这时链表首尾相连成环
fast.next = head;
// 新的头节点是慢指针所指节点的下一个节点
head = slow.next;
// 慢指针所指节点的的后继指针指向null
// 断开环
slow.next = null;
return head;
}
private int calculateLen(ListNode head){
int len = 0;
while (head!=null) {
head = head.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
}
64最小路径和
给定一个包含非负整数的
m x n网格grid。请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(i == 0 && j == 0) {
continue;
} else if(i == 0) {
grid[i][j] = grid[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j];
} else if(j == 0) {
grid[i][j] = grid[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j];
} else {
grid[i][j] = Math.min(grid[i - 1][j], grid[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
}
return grid[grid.length - 1][grid[0].length - 1];
}
}
66加一
给定一个由 整数 组成的 非空 数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
最高位数字存放在数组的首位,数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
int n = digits.length;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (digits[i] != 9) {
++digits[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
digits[j] = 0;
}
return digits;
}
}
// digits 中所有的元素均为 9
int[] ans = new int[n + 1];
ans[0] = 1;
return ans;
}
}
70爬楼梯
假设正在爬楼梯,需要
n阶才能到达楼顶。每次可以爬
1或2个台阶。有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int a = 1, b = 1, sum;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
sum = a + b;
a = b;
b = sum;
}
return b;
}
}
75颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共
n个元素的数组nums,原地 对它们进行排序。
- 使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
使用整数
0、1和2分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return;
}
int p0 = 0, p2 = nums.length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i<= p2;i++) {
//当我们将nums[i]与nums[p2]进行交换之后,新的nums[i]可能仍然是2
while (i <= p2 && nums[i] == 2) {
swap(nums, i, p2);
p2--;
}
if (nums[i] == 0) {
swap(nums, i, p0);
p0++;
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int temp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = temp;
}
}
78子集
给一个整数数组
nums,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(0, nums, res, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int i, int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> tmp) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {
tmp.add(nums[j]);
backtrack(j + 1, nums, res, tmp);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
82删除排序链表中的重复元素II
给定一个已排序的链表的头
head,删除原始链表中所有重复数字的节点,只留下不同的数字。返回 已排序的链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int x = cur.next.val;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == x) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
83删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个已排序的链表的头
head,删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次。返回 已排序的链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
88合并两个有序数组
给两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组
nums1和nums2,另有两个整数m和n。
- 分别表示
nums1和nums2中的元素数目。请 合并
nums2到nums1中,使合并后的数组同样按 非递减顺序 排列。
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int p1 = m - 1;
int p2 = n - 1;
int p = n + m - 1;
while (p1 >= 0 && p2 >= 0) {
nums1[p--] = (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2] ? nums2[p2--] : nums1[p1--]);
}
while (p2 >= 0) {
nums1[p--] = nums2[p2--];
}
}
}
92反转链表II
给单链表的头指针
head和两个整数left和right,其中left <= right。请反转从位置
left到位置right的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。第一步:
- 找到待反转节点的前一个节点。
第二步:
- 反转 m 到 n 这部分。
第三步:
- 将反转的起点的
next指向反转的后面一部分。第四步:
- 将第一步找到的节点指向反转以后的头节点。

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
res.next = head;
ListNode node = res;
//找到需要反转的那一段的上一个节点。
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
//node.next就是需要反转的这段的起点
ListNode nextHead = node.next;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode pre = null;
//反转m到n这一段
for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
next = nextHead.next;
nextHead.next = pre;
pre = nextHead;
nextHead = next;
}
//将反转的起点的next指向next
node.next.next = next;
//需要反转的那一段的上一个节点的next节点指向反转后链表的头结点
node.next = pre;
return res.next;
}
}
94二叉树的中序遍历
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, result);
return result;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, result);
result.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, result);
}
}
时间复杂度:
O(n),其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数,二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。空间复杂度:
O(n),空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到O(n)的级别。
栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(root!=null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
result.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return result;
}
}
98验证二叉搜索树
给一个二叉树的根节点
root,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
// 访问左子树
if (!isValidBST(root.left)) {
return false;
}
// 访问当前节点:如果当前节点小于等于中序遍历的前一个节点,说明不满足BST,返回 false;否则继续遍历
if (root.val <= pre) {
return false;
}
pre = root.val;
// 访问右子树
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
103二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。
- 即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
//创建队列,保存节点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);//先把节点加入到队列中
boolean leftToRight = true;//第一步先从左边开始打印
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//记录每层节点的值
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
//统计这一层有多少个节点
int count = queue.size();
//遍历这一层的所有节点,把他们全部从队列中移出来,顺便
//把他们的值加入到集合level中,接着再把他们的子节点(如果有)
//加入到队列中
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//poll移除队列头部元素(队列在头部移除,尾部添加)
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
//判断是从左往右打印还是从右往左打印
if (leftToRight) {
//如果从左边打印,直接把访问的节点值加入到列表level的末尾即可
level.add(node.val);
} else {
//如果是从右边开始打印,每次要把访问的节点值
//加入到列表的最前面
level.add(0, node.val);
}
//左右子节点如果不为空会被加入到队列中
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
//把这一层的节点值加入到集合res中
res.add(level);
//改变下次访问的方向
leftToRight = !leftToRight;
}
return res;
}
}
105从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组
preorder和inorder,其中preorder是二叉树的先序遍历
inorder是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。理解遍历顺序:
先序遍历(preorder):根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
中序遍历(inorder):左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
利用先序遍历的第一个元素作为根节点:
- 先序遍历的第一个元素总是当前子树的根节点。
在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置:
- 这个位置将中序遍历分为左子树和右子树。
递归构建左子树和右子树:
使用中序遍历中根节点左侧的数组构建左子树
- 使用先序遍历中根节点之后的元素构建左子树
使用中序遍历中根节点右侧的数组构建右子树
- 使用先序遍历中左子树之后(即根节点之后紧接着的元素)的元素构建右子树。
递归终止条件:
- 当先序遍历或中序遍历的数组为空时,返回
null。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || inorder == null || preorder.length != inorder.length) {
return null;
}
return buildTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// 先序遍历的第一个元素是根节点
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
int rootIndexInorder = inStart;
while (inorder[rootIndexInorder] != rootVal) {
rootIndexInorder++;
}
// 构建左子树和右子树
int leftSubtreeSize = rootIndexInorder - inStart;
root.left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSubtreeSize, inorder, inStart, rootIndexInorder - 1);
root.right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + leftSubtreeSize + 1, preEnd, inorder, rootIndexInorder + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
108将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
给一个整数数组
nums,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请将其转换为一棵 平衡二叉搜索树。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode dfs(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
if (lo > hi) {
return null;
}
// 以升序数组的中间元素作为根节点 root。
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
// 递归的构建 root 的左子树与右子树。
root.left = dfs(nums, lo, mid - 1);
root.right = dfs(nums, mid + 1, hi);
return root;
}
}
112路径总和
给二叉树的根节点
root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和
targetSum。
- 如果存在,返回
true,否则,返回false。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) {
return false;
}
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {
return sum-root.val == 0;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left,sum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,sum-root.val);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数,对每个节点访问一次。
113路径总和II
给二叉树的根节点
root和一个整数目标和targetSum,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
采用深度优先搜索的方式,遍历每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,就找到了一条满足条件的路径。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
dfs(root, sum);
return result;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
sum = sum - root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
}
dfs(root.left, sum);
dfs(root.right, sum);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
时间复杂度:
O(N^2),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度:
O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数,空间复杂度主要取决于栈空间的开销,栈中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
114二叉树展开为链表
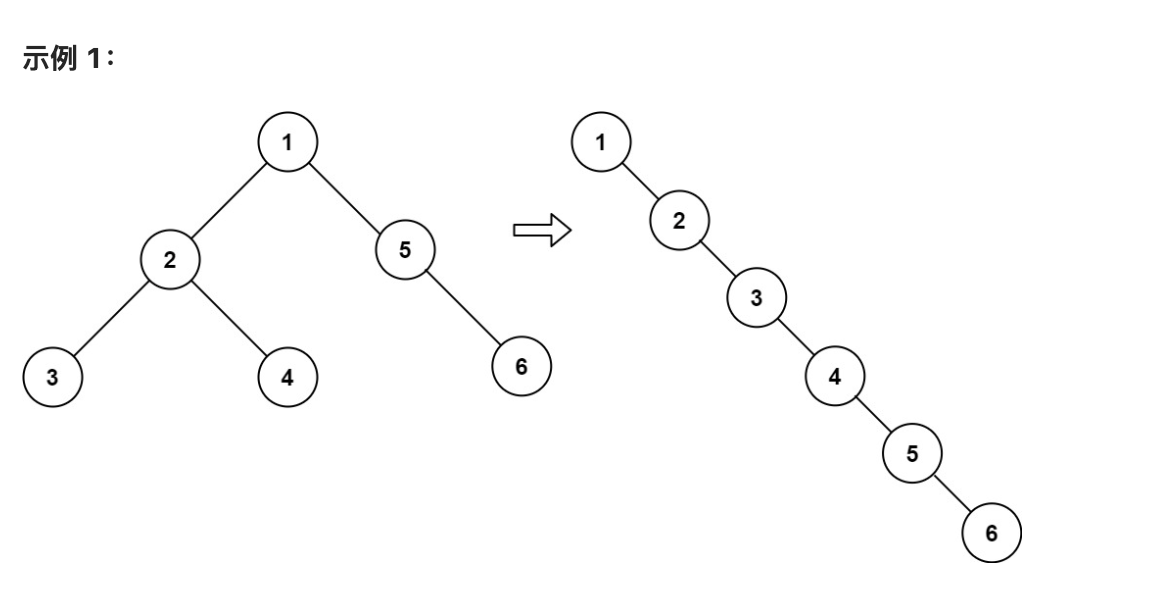
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
// 左子树为 null,直接考虑下一个节点
if (root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
} else {
// 找左子树最右边的节点
TreeNode pre = root.left;
while (pre.right != null) {
pre = pre.right;
}
// 将原来的右子树接到左子树的最右边节点
pre.right = root.right;
// 将左子树插入到右子树的地方
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
// 考虑下一个节点
root = root.right;
}
}
}
}
121买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组
prices,它的第i个元素prices[i]表示一支给定股票第i天的价格。只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。
- 设计一个算法来计算所能获取的最大利润。
返回可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。
如果不能获取任何利润,返回
0。
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] < minPrice) {
minPrice = prices[i];
} else if (prices[i] - minPrice > maxProfit) {
maxProfit = prices[i] - minPrice;
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
122买卖股票的最佳时机II
给一个整数数组
prices,其中prices[i]表示某支股票第i天的价格。在每一天,可以决定是否购买和/或出售股票。
在任何时候 最多 只能持有 一股 股票。
- 也可以先购买,然后在 同一天 出售。
返回 能获得的 最大 利润 。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int temp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
if (temp > 0) {
profit += temp;
}
}
return profit;
}
}
125验证回文串
如果在将所有大写字符转换为小写字符、并移除所有非字母数字字符之后,短语正着读和反着读都一样。
- 则可以认为该短语是一个 回文串 。
字母和数字都属于字母数字字符。
给一个字符串
s,如果它是 回文串 ,返回true,否则,返回false。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length() -1;
while(left<right) {
while(left<right&&!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) {
left++;
}
while(left<right&&!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) {
right--;
}
if (left<right&&Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(left))!=Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(right))) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}
129求根节点到叶节点数字之和
给一个二叉树的根节点
root,树中每个节点都存放有一个0到9之间的数字。每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int prevSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum;
} else {
return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum);
}
}
}
时间复杂度:
- O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数,对每个节点访问一次。
空间复杂度:
- O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间,递归栈的深度等于二叉树的高度,最坏情况下,二叉树的高度等于节点个数,空间复杂度为
O(n)。
136只出现一次的数字
给一个 非空 整数数组
nums,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int result = 0;
for(int num : nums) {
result = result ^ num;
}
return result;
}
}
141环形链表
给一个链表的头节点
head,判断链表中是否有环。使用两个快慢指针遍历链表。
slow每次走一步,fast每次走两步。fast走到链表尾部无环,slow与fast重叠则有环。若链表的起始位置等于环的起始位置:
slow走一圈回到起始位置,fast刚好走了两圈。若环的起始位置在链表的其他位置:
- 待
slow走到环的起始位置,fast在环的任意位置,可以看成是起点不同的遍历。- 此时
slow在走一圈范围内肯定会被fast超越。- 因为每当
fast每次移动一次,fast都会靠近slow一步,如果带环,两者肯定会重叠。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
142环形链表II
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
fast = head;
while(slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
143重排链表
给定一个单链表
L的头节点head,单链表L表示为:L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
目标链表即为:将原链表的左半端和反转后的右半端合并后的结果。
找到原链表的中点
我们可以使用快慢指针来
O(N)找到链表的中间节点将原链表的右半端反转
将原链表的两端合并
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
//1.找到链表中间节点
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
//2.反转右端链表节点
l2 = reverseList(l2);
//3.链表两端合并
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
public void mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode tempL1;
ListNode tempL2;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
tempL1 = l1.next;
tempL2 = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l1 = tempL1;
l2.next = l1;
l2 = tempL2;
}
}
}
144二叉树的前序遍历
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, result);
preorder(root.right, result);
}
}
栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(root!=null) {
result.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return result;
}
}
145二叉树的后序遍历
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, result);
postorder(root.right, result);
result.add(root.val);
}
}
栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//左,右,根
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (root!=null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(root!=null) {
result.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.left;
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
146LRU缓存机制
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public class LRUCache {
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进哈希表
cache.put(key, newNode);
// 添加至双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除哈希表中对应的项
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
} else {
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}
148排序链表
给链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//使用快慢指针找到中点
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while(fast!=null && fast.next !=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//分割为两个链表
ListNode newList = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
//将两个链表继续分割
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(newList);
ListNode leftHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode result = leftHead;
//归并排序
while(left != null && right != null){
if(left.val < right.val){
leftHead.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else{
leftHead.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
leftHead = leftHead.next;
}
//判断左右链表是否为空
leftHead.next = (left != null ? left : right);
return result.next;
}
}
时间复杂度:
O(nlogn),其中 n 是链表的长度。
155最小栈
设计一个支持
push,pop,top操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(minStack.isEmpty() || x <= minStack.peek()) {
minStack.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
if(stack.pop().equals(minStack.peek())) {
minStack.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
155将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表
将一个 二叉搜索树 就地转化为一个 已排序的双向循环链表 。
对于双向循环列表,可以将左右孩子指针作为双向循环链表的前驱和后继指针。
第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
dfs(cur): 递归法中序遍历
终止条件: 当节点 cur 为空,代表越过叶节点,直接返回
递归左子树,即 dfs(cur.left)
构建链表:
当 pre 为空时: 代表正在访问链表头节点,记为 head
当 pre 不为空时: 修改双向节点引用,即 pre.right = cur ,cur.left = pre
保存 cur : 更新 pre = cur ,即节点 cur 是后继节点的 pre
递归右子树,即 dfs(cur.right)
treeToDoublyList(root):
特例处理: 若节点 root 为空,则直接返回
初始化: 空节点 pre
转化为双向链表: 调用 dfs(root)
构建循环链表: 中序遍历完成后,head 指向头节点,pre 指向尾节点,因此修改 head 和 pre 的双向节点引用即可
返回值: 返回链表的头节点 head 即可
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
Node head, pre;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null) return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right = head;
head.left =pre;//进行头节点和尾节点的相互指向,这两句的顺序也是可以颠倒的
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
//pre用于记录双向链表中位于cur左侧的节点,即上一次迭代中的cur,当pre==null时,cur左侧没有节点,即此时cur为双向链表中的头节点
if(pre==null) head = cur;
//反之,pre!=null时,cur左侧存在节点pre,需要进行pre.right=cur的操作。
else pre.right = cur;
cur.left = pre;//pre是否为null对这句没有影响,且这句放在上面两句if else之前也是可以的。
pre = cur;//pre指向当前的cur
dfs(cur.right);//全部迭代完成后,pre指向双向链表中的尾节点
}
}
160相交链表
给两个单链表的头节点
headA和headB。请找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回
null。
双指针
创建两个指针 pA 和 pB,分别初始化为链表 A 和 B 的头结点。然后让它们向后逐结点遍历。
当 pA到达链表的尾部时,将它重定位到链表 B 的头结点,类似的,当 pB到达链表的尾部时,将它重定位到链表 A 的头结点。
若在某一时刻 pA和 pB 相遇,则 pA/pB为相交结点。
考虑以下两个链表: A={1,3,5,7,9,11} 和 B={2,4,9,11},相交于结点 9。
由于
B.length (=4) < A.length (=6),pB比 pA少经过 2个结点,会先到达尾部。将 pB重定向到 A 的头结点,pA重定向到 B 的头结点后,pB要比 pA多走 2 个结点。
因此,它们会同时到达交点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode head1 = headA;
ListNode head2 = headB;
while (head1 != head2) {
if (head1 != null) {
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
head1 = headB;
}
if (head2 != null) {
head2 = head2.next;
} else {
head2 = headA;
}
}
return head1;
}
}
时间复杂度 : O(m+n)。
空间复杂度 : O(1)。
162寻找峰值
峰值元素是指其值严格大于左右相邻值的元素。
给一个整数数组
nums,找到峰值元素并返回其索引。数组可能包含多个峰值,在这种情况下,返回 任何一个峰值 所在位置即可。
二分查找
查找时,左指针 l,右指针 r,以其保持左右顺序为循环条件。
根据左右指针计算中间位置 m,并比较 m 与 m+1 的值,如果 m 较大,则左侧存在峰值,r = m。
如果 m + 1 较大,则右侧存在峰值,l = m + 1。
public class Solution {
public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
int l = 0, r = nums.length - 1;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
}
215数组中的第K个最大元素
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
return quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length - k);
}
public int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right){
int pivot = nums[left];
while(left < right){
while(left < right && nums[right] >= pivot){
right--;
}
nums[left] = nums[right];
while(left < right && nums[left] <= pivot){
left++;
}
nums[right] = nums[left];
}
nums[left] = pivot;
return left;
}
public int quickSort(int[] nums, int left, int right, int k){
// 如果经过一轮快排分区后pivot位置刚好是k,那么可以直接退出了
int mid = partition(nums, left, right);
if(mid == k){
return nums[k];
}else if(mid > k){
return quickSort(nums, left, mid - 1, k);
}else{
return quickSort(nums, mid + 1, right, k);
}
}
}
时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度 O(1)。
222完全二叉树的节点个数
给一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点
root,求出该树的节点个数。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int lh = 0, rh = 0;
TreeNode left = root, right = root;
// 求左高
while (left != null) {
left = left.left;
lh++;
}
// 求右高
while (right != null) {
right = right.right;
rh++;
}
// 以 root 为根节点的树是「满二叉树」
if (lh == rh) {
return (int) Math.pow(2, lh) - 1;
}
// 否则,按照正常方式遍历
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
229求众数II
给定一个大小为 n 的整数数组,找出其中所有出现超过
⌊ n/3 ⌋次的元素。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> majorityElement(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return res;
}
// 初始化两个候选人candidate,和他们的计票
int cand1 = nums[0], count1 = 0;
int cand2 = nums[0], count2 = 0;
// 摩尔投票法,分为两个阶段:配对阶段和计数阶段
// 配对阶段
for (int num : nums) {
// 投票
if (cand1 == num) {
count1++;
continue;
}
if (cand2 == num) {
count2++;
continue;
}
// 第1个候选人配对
if (count1 == 0) {
cand1 = num;
count1++;
continue;
}
// 第2个候选人配对
if (count2 == 0) {
cand2 = num;
count2++;
continue;
}
count1--;
count2--;
}
// 计数阶段
// 找到了两个候选人之后,需要确定票数是否满足大于 N/3
count1 = 0;
count2 = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (cand1 == num) {
count1++;
} else if (cand2 == num) {
count2++;
}
}
if (count1 > nums.length / 3) {
res.add(cand1);
}
if (count2 > nums.length / 3) {
res.add(cand2);
}
return res;
}
}
230二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
中序遍历
二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的,因此只需要对二叉搜索树执行中序遍历,并返回第 k 小的值即可。
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Deque<TreeNode> d = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (root != null || !d.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
d.addLast(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = d.pollLast();
if (--k == 0) {
return root.val;
}
root = root.right;
}
return -1;
}
}
时间复杂度:
令 h 为树高,先到达叶子位置(最小节点位置),复杂度为 O(h),然后找到第 k 小的元素,复杂度为 O(k)。
整体复杂度为 O(h + k)。
空间复杂度:
- 令 h 为树高,复杂度为 O(h)。
class Solution {
int res, k;
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
dfs(root.left);
if (k == 0) return;
if (--k == 0) res = root.val;
dfs(root.right);
}
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
}
234回文链表
整个流程可以分为以下步骤:
找到前半部分链表的尾节点。
反转后半部分链表。
判断是否回文。
恢复链表。
返回结果。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
// 找到前半部分链表的尾节点并反转后半部分链表
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverseList(firstHalfEnd.next);
// 判断是否回文
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
while (result && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
result = false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
// 还原链表并返回结果
firstHalfEnd.next = reverseList(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
237删除链表中的节点
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
257二叉树的所有路径
给一个二叉树的根节点
root,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
constructPaths(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
StringBuffer pathBuilder = new StringBuffer(path);
pathBuilder.append(String.valueOf(root.val));
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
paths.add(pathBuilder.toString());
} else {
pathBuilder.append("->");
constructPaths(root.left, pathBuilder.toString(), paths);
constructPaths(root.right, pathBuilder.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
时间复杂度:
O(N^2),其中 N表示节点数目。空间复杂度:
O(N^2),其中 N表示节点数目。
300最长上升子序列
给一个整数数组
nums,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] 输出:4 解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0;i<nums.length;i++) {
for (int j = 0;j<i;j++) {
if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
result = Math.max(result, dp[i]);
}
return result;
}
}
344反转字符串
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
char temp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
371两整数之和
class Solution {
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int carry = (a & b) << 1;
a = a ^ b;
b = carry;
}
return a;
}
}
378有序矩阵中第K小的元素
给一个
n x n矩阵matrix,其中每行和每列元素均按升序排序,找到矩阵中第k小的元素。请注意,它是 排序后 的第
k小元素,而不是第k个 不同 的元素。
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int left = matrix[0][0];
int right = matrix[row - 1][col - 1];
while (left < right) {
// 每次循环都保证第K小的数在start~end之间,当start==end,第k小的数就是start
// 防溢出,也可以写做mid = (right +left) >> 1;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 找二维矩阵中<=mid的元素总个数
int count = findLessThanMid(matrix, mid, row, col);
if (count < k) {
// 第k小的数在右半部分,且不包含mid
left = mid + 1;
} else {
// 第k小的数在左半部分,可能包含mid
right = mid;
}
}
return right;
}
private int findLessThanMid(int[][] matrix, int mid, int row, int col) {
// 以列为单位找,找到每一列最后一个<=mid的数即知道每一列有多少个数<=mid
int i = row - 1;
int j = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < col) {
if (matrix[i][j] <= mid) {
// 第j列有i+1个元素<=mid
count += i + 1;
j++;
} else {
// 第j列目前的数大于mid,需要继续在当前列往上找
i--;
}
}
return count;
}
}
时间复杂度:
O(nlog(r−l)),二分查找进行次数为O(log(r−l)),每次操作时间复杂度为O(n)。空间复杂度:
O(1)。
387字符串中的第一个唯一字符
给定一个字符串
s,找到 它的第一个不重复的字符,并返回它的索引 。如果不存在,则返回
-1。
class Solution {
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int val = map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0);
map.put(s.charAt(i), val + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1) return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
415字符串相加
class Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("");
int i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1, carry = 0;
while(i >= 0 || j >= 0){
int n1 = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0;
int n2 = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0;
int tmp = n1 + n2 + carry;
carry = tmp / 10;
res.append(tmp % 10);
i--;
j--;
}
if(carry == 1) {
res.append(1);
}
return res.reverse().toString();
}
}
437路径总和III
给定一个二叉树的根节点
root,和一个整数targetSum。求该二叉树里节点值之和等于
targetSum的 路径 的数目。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int result = 0;
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
dfs(root, targetSum);
pathSum(root.left, targetSum);
pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
return result;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, long targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
if(root.val == targetSum) {
result++;
}
dfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
dfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
}
448找到所有数组中消失的数字
给一个含
n个整数的数组nums,其中nums[i]在区间[1, n]内。请找出所有在
[1, n]范围内但没有出现在nums中的数字,并以数组的形式返回结果。遍历每个元素,对索引进行标记
- 将对应索引位置的值变为负数
遍历下索引,看看哪些索引位置上的数不是负数的
- 位置上不是负数的索引,对应的元素就是不存在的
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
//用来存放结果
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历下数组的元素,对对应的索引位置的元素作标记
int len = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int num = Math.abs(nums[i]); //由于数组的元素有可能被*-1,所以取绝对值
int index = num - 1;
if(nums[index] > 0){
nums[index] *= -1;
}
}
// 寻找没有标记的索引位置
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
if(nums[i] > 0){
int num = i + 1; //将索引转化为对应的元素
res.add(num);
}
}
return res;
}
}
450删除二叉搜索树中的节点
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。
返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点;
如果找到了,删除它。
二叉搜索树的性质:
- 左子树的节点的值小于根节点的值,右子树的节点大于根节点的值。
当root的值和key相等时,有四种情况:





/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val > key) {
//当前节点的值大于目标值 递归去左子树寻找
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
//当前节点的值小于目标值 递归去右子树寻找
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else {
//情况一可以和二三合并处理
//情况二
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
}
//情况三
if (root.right == null) {
return root.left;
}
//情况四
//找到右节点的左子树中为空的位置
TreeNode rightNode = root.right;
while (rightNode.left != null) {
rightNode = rightNode.left;
}
rightNode.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
}
return root;
}
}
560和为K的子数组
给一个整数数组
nums和一个整数k。请统计并返回 该数组中和为
k的子数组的个数。前缀和
哈希表中存放的是前缀和对应的个数,答案
res中记录着每个前缀和sum[i] -k的个数
public class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int count = 0, pre = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>();
mp.put(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre += nums[i];
if (mp.containsKey(pre - k)) {
count += mp.get(pre - k);
}
mp.put(pre, mp.getOrDefault(pre, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}
}
572另一棵树的子树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
return dfs(s, t);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null) {
return false;
}
return check(s, t) || dfs(s.left, t) || dfs(s.right, t);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null && t == null) {
return true;
}
if (s == null || t == null || s.val != t.val) {
return false;
}
return check(s.left, t.left) && check(s.right, t.right);
}
}
662二叉树最大宽度
给一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回树的 最大宽度 。树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。
此题求二叉树所有层的最大宽度,比较直观的方法是求出每一层的宽度,然后求出最大值。
求每一层的宽度时,因为两端点间的
null节点也需要计入宽度,因此可以对节点进行编号。一个编号为
index的左子节点的编号记为2×index,右子节点的编号记为2×index+1,计算每层宽度时,用每层节点的最大编号减去最小编号再加 1 即为宽度。遍历节点时,可以用广度优先搜索来遍历每一层的节点,并求出最大值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 根节点编号为 0
root.val = 0;
queue.add(root);
int sum;
int ans = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
sum = queue.size();
// 队头和队尾的编号值求差用来更新宽度
ans = Math.max(ans, queue.getLast().val - queue.getFirst().val + 1);
// 一次处理一层,进入这个循环前队列中是一层的所有非空节点
while(sum > 0) {
TreeNode temp = queue.remove();
// 子节点入队前修改 val, val = 满二叉树中节点编号
if(temp.left != null) {
queue.add(temp.left);
temp.left.val = temp.val * 2 + 1;
}
if(temp.right != null) {
queue.add(temp.right);
temp.right.val = temp.val * 2 + 2;
}
sum--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
674最长连续递增序列
给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且 连续递增的子序列,并返回该序列的长度。
class Solution {
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int count = 1, result = 1;
for (int i =0;i<nums.length - 1;i++){
if (nums[i] < nums[i+1]){
count++;
}else {
count = 1;
}
result = Math.max(result , count);
}
return result;
}
}
704二分查找
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums==null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left<=right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[middle]==target) {
return middle;
} else if (nums[middle] > target) {
right = middle - 1;
} else {
left = middle + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
718最长重复子数组
给两个整数数组
nums1和nums2,返回 两个数组中 公共的 长度最长的子数组的长度。输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,2,1], nums2 = [3,2,1,4,7] 输出:3 解释:长度最长的公共子数组是 [3,2,1]
动态规划
首先定义
dp[i][j]表示为A[i:]和B[j:]的最长公共前缀。
dp[i][j]可以从dp[i+1][j+1]转移而来。
class Solution {
public int findLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n = nums1.length;
int m = nums2.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][m+1];//dp[i][j]表示从i开始的A的子串和从j开始的B的子串的最长公共前缀
int maxs = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
if(nums1[i-1] == nums2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}else{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
maxs = Math.max(maxs, dp[i][j]);
}
}
return maxs;
}
}
876链表的中间结点
快慢指针法
用两个指针
slow与fast一起遍历链表。
slow一次走一步,fast一次走两步。那么当
fast到达链表的末尾时,slow必然位于中间。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
958二叉树的完全性检验
给一棵二叉树的根节点
root,请判断这棵树是否是一棵 完全二叉树 。
class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode prev = root;
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
if (prev == null && node != null) {
return false;
}
if (node != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
prev = node;
}
return true;
}
}
1214查找两颗二分搜索树之和
给出两棵二叉搜索树,请你从两棵树中各找出一个节点,使得这两个节点的值之和等于目标值 Target。
如果可以找到返回 True,否则返回 False。
示例 1:
输入:root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3], target = 5 输出:true 解释:2 加 3 和为 5。
二分法解决:
先固定一棵树的一个节点,将目标值Target减去这个节点的值,得到新的目标值target。
将这个新的目标值和另外一棵树进行比较,利用二分搜索数的特性进行查找命中,从根节点开始,如果新的目标值target和根节点的值相等,则直接返回true。
如果新的目标值比根节点小,进行左递归查找,如果新的目标值比根节点大,进行右递归。
依次类推,直到树底下的节点为空,才返回false。
固定一棵树的一个节点,查找另一棵树的节点的时间复杂度是
O(logn)。因为一棵树需要遍历,时间复杂度是
O(nlogn)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean twoSumBSTs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2, int target) {
if (!root1) return false;
if (find(root2, target - root1.val)) return true;
return twoSumBSTs(root1.left, root2, target) ||
twoSumBSTs(root1.right, root2, target);
}
private boolean find(TreeNode node, int target) {
if (!node) return false;
if (node.val == target) return true;
else if (target < node.val) return find(node.left, target);
else return find(node.right, target);
}
}
1539第K个缺失的正整数
设:
arr = [2,3,4,5,7,11], k = 5可以利用数组下标来得到该位置之前缺失的元素数量,例如:
i = 0,此时数组元素
arr[i] = 2,在0位置上,不缺失的情况下,对应的元素应该是1,所以缺失个数为arr[i] - i - 1 = 1,因为数组下标是从0开始的,而元素是从1开始的,所以计算个数的时候,除了减掉下标值之外,还需要再减1。按照这个方式,能计算出该数组的每个元素对应的缺失元素个数:

在这个序列中,能够通过二分查找,找到k所对应的位置,有了这个位置,就能通过对应的元素找到缺失的第k个整数。
举例来说,如果要找到k = 5,第5个缺失的元素,那么需要从一个确定的数向后或向前推算:
对于2,3,4来说,它们之前缺少1个元素,所以不考虑这些元素。
对于7来说,它之前缺少3个元素,那么从它开始往后推2个元素,就有可能是缺失的第5个元素。
前提是它后面的元素缺失数量要大于k = 5。
对于11来说,它之前缺少6个元素,要找的第5个元素,一定是在它之前缺失的,那从它开始往前推2个元素(第6个,第5个),就是要找的缺失的第5个元素。
根据这种分析,就可以在这个缺失数量的序列上进行二分查找,确定一个区间
[i,j],满足lack[i] < k <= lack[j],则第k个缺失的数为k - (arr[i] - i - 1) + arr[i],arr[i] - i - 1表示arr[i]位置缺少的元素个数,k - 缺失个数表示从arr[i]开始还缺少几个元素,再加上arr[i],就是第k个缺失的元素。
class Solution {
public int findKthPositive(int[] arr, int k) {
// 第一个数比缺失的数要大的话,直接返回k
if(arr[0] > k){
return k;
}
// 找到缺失数量大于k的最小的位置
int left = 0, right = arr.length;
while(left < right){
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int x = mid < arr.length ? arr[mid] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(x - mid - 1 >= k){
right = mid;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 第k个缺失的数 - (最小位置之前的那个数所缺失的个数) + 最小位置前面的那个数
// 5 - (7 - 3 - 1) + 7 = 第五个缺失的数 - 7前面有3个缺失的数 + 7
return k - (arr[left - 1] - (left - 1) - 1) + arr[left - 1];
}
}
public int findKthPositive(int[] arr, int k) {
int n = arr.length; // 数组长度
int low = 0, high = n; // 初始化二分查找的上下边界
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2; // 计算中间位置
// 计算当前中间位置缺失的正整数数量
if (arr[mid] - mid - 1 >= k) {
high = mid; // 如果缺失数量大于或等于 k,则目标在左半部分
} else {
low = mid + 1; // 否则,目标在右半部分
}
}
// 计算当前 low 之前缺失的正整数数量
int prev = low > 0 ? arr[low - 1] : 0;
int prevMissingCount = prev - low;
return prev + k - prevMissingCount; // 计算并返回第 k 个缺失的正整数
}
1143最长公共子序列
定义一个二维数组 dp 用来存储最长公共子序列的长度,其中
dp[i][j]表示 S1 的前 i 个字符与 S2 的前 j 个字符最长公共子序列的长度。
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int n1 = text1.length(), n2 = text2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n1+1][n2+1];
for (int i = 1;i <= n1;i++) {
for (int j = 1;j<=n2;j++) {
if(text1.charAt(i-1) == text2.charAt(j-1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n1][n2];
}
}
1614括号的最大嵌套深度
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(String s) {
int ans = 0, size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') {
++size;
ans = Math.max(ans, size);
} else if (ch == ')') {
--size;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏